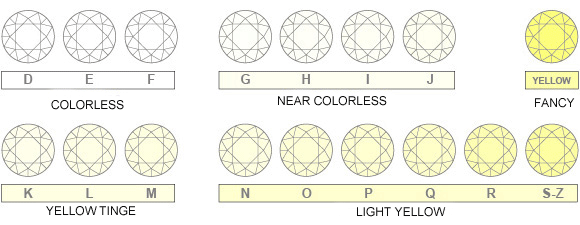
The finest quality as per color grading is totally colorless, which is graded as “D” color diamond across the globe, meaning it is absolutely free from any color. The next grade has a very slight trace of color, which can be observed by any expert diamond valuer/grading laboratory. However when studded in jewellery these very light colored diamonds do not show any color or it is not possible to make out color shades. These are graded as E color or F color diamonds.
Diamonds which show very little traces of color are graded as G or H color diamonds. Slightly colored diamonds are graded as I or J or K color. A diamond can be found in any color in addition to colorless. Some of the colored diamonds, such as pink, are very rare.
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond is perfectly transparent with no hue, or color. However, in reality most gem-sized natural diamonds are imperfect. The color of a diamond may be affected by chemical impurities and/or structural defects in the crystal lattice. Depending on the hue and intensity of a diamond’s coloration, a diamond’s color can either detract from or enhance its value. For example, most white diamonds are discounted in price as more yellow hue is detectable, while intense pink or blue diamonds (such as the Hope Diamond) can be dramatically more valuable. The Aurora Diamond Collection displays a spectacular array of naturally colored diamonds, which occur in every color of the rainbow.
Most diamonds used as gemstones are basically transparent with little tint, or white diamonds. The most common impurity, nitrogen, replaces a small proportion of carbon atoms in a diamond’s structure and causes a yellowish to brownish tint. This effect is present in almost all white diamonds; in only the rarest diamonds is the coloration from this effect undetectable. The GIA has developed a rating system for color in white diamonds, from “D” to “Z” (with D being “colorless” and Z having a bright yellow coloration), which has been widely adopted in the industry and is universally recognized, superseding several older systems. The GIA system uses a benchmark set of natural diamonds of known color grade, along with standardized and carefully controlled lighting conditions. Diamonds with higher color grades are rarer, in higher demand, and therefore more expensive, than lower color grades. Oddly enough, diamonds graded Z are also rare, and the bright yellow color is also highly valued. Diamonds graded D-F are considered “colorless”, G-J are considered “near-colorless”, K-M are “slightly colored”. N-Y usually appear light yellow or brown.
In contrast to yellow or brown hues, diamonds of other colors are more rare and valuable. While even a pale pink or blue hue may increase the value of a diamond, more intense coloration is usually considered more desirable and commands the highest prices. A variety of impurities and structural imperfections cause different colors in diamonds, including yellow, pink, blue, red, green, brown, and other hues. Diamonds with unusual or intense coloration are sometimes labeled “fancy” in the diamond industry. Intense yellow coloration is considered one of the fancy colors, and is separate from the color grades of white diamonds. Gemologists have developed rating systems for fancy colored diamonds, but they are not in common use because of the relative rarity of such diamonds.